Explanation of the concept
What is X-SeeO₂?
X-SeeO₂ is an ambitious EIC project that develops advanced X-ray technologies to help transform cement — one of the world’s largest CO₂ emitters — into a CO₂-absorbing material.
At the core of X-SeeO₂ lies access to synchrotron and laboratory X-ray analytical methods that reveal, in real time, how cementitious materials react, harden, and capture CO₂.
These insights allow researchers and industry to optimise processes, scale up green technologies, and design next-generation sustainable cements.
Our Mission
To make cement and concrete part of the climate solution, not the problem — by providing cutting-edge analytical tools, data workflows, and real-world validation of CO₂-absorbing materials.

Overall Contribution
Expected Outcomes
Objectives & Methodologies
Key features targeting success
X-SeeO₂ aims to accelerate innovations for the decarbonisation of cement and the smart carbonation of concretes.
The project combines advanced synchrotron-based and laboratory X-ray analysis with innovative workflows, outreach, and real-world validation.

Objective 1
Enabling Technology
Provide access to state-of-the-art X-ray analytical techniques [X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD) and microtomography (μCT)] and data analysis tools to advance understanding of cementitious materials.
Objective 2
Workflow Development
Design and validate synchrotron-compatible in-situ carbonation cells [XRPD & μCT] and standardised analytical workflows to ensure robust, comparable and reliable data.
Objective 3
Outreach & Training
Deliver training and dissemination activities to share methodologies and results across the Challenge project portfolio.

Objective 4
Case Study 1
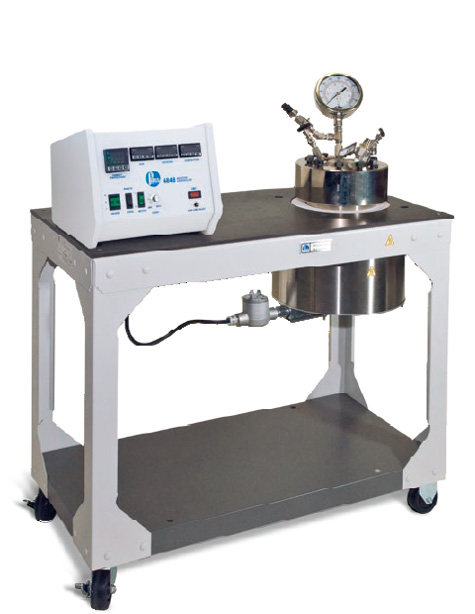
Investigate mechanochemical activation (MCA) of industrial wastes under CO₂ conditions to develop new supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs).
Objective 5
Case Study 2
Develop and test autoclave CO₂-cured binders and innovative SCMs under varied experimental conditions to optimise performance and sustainability.
Core Technologies
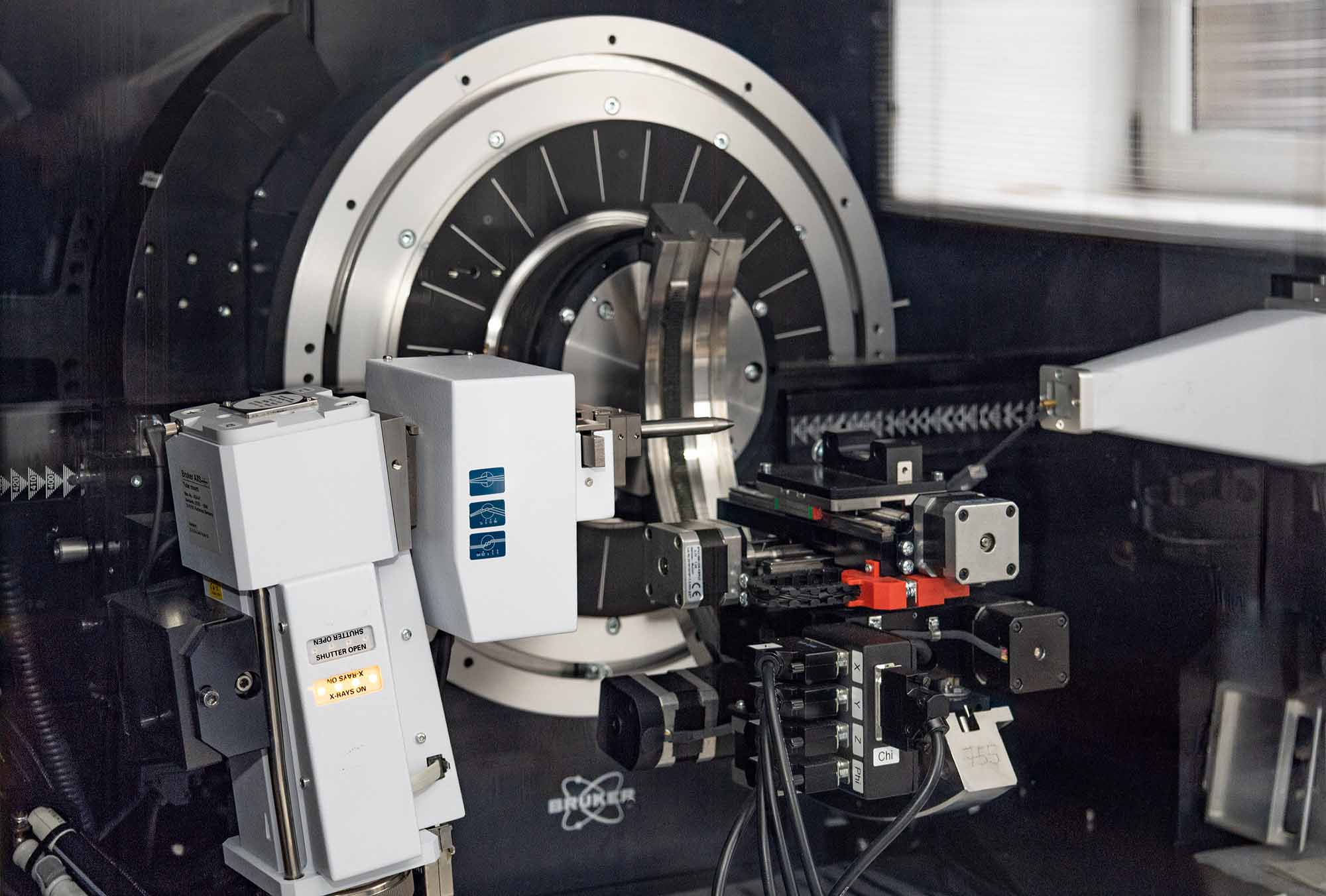

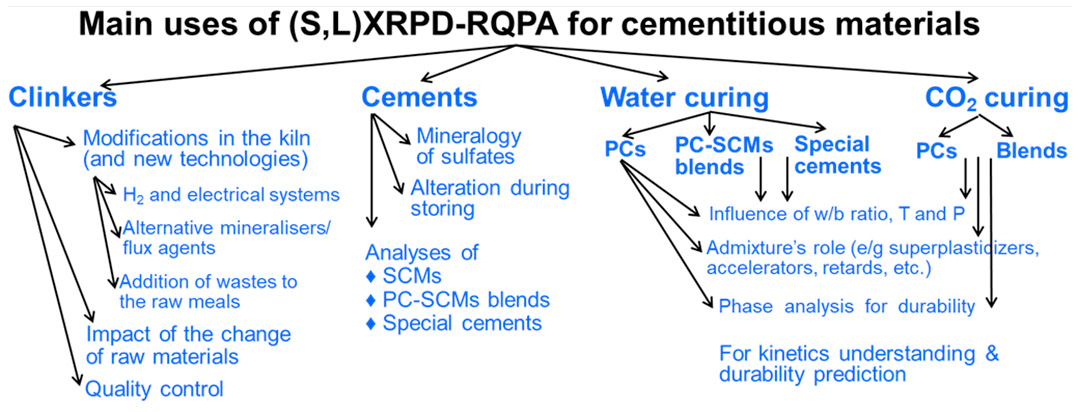
X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD) Tracks crystalline and amorphous phase evolution during hydration and CO₂ mineralisation — revealing how materials react and transform over time.
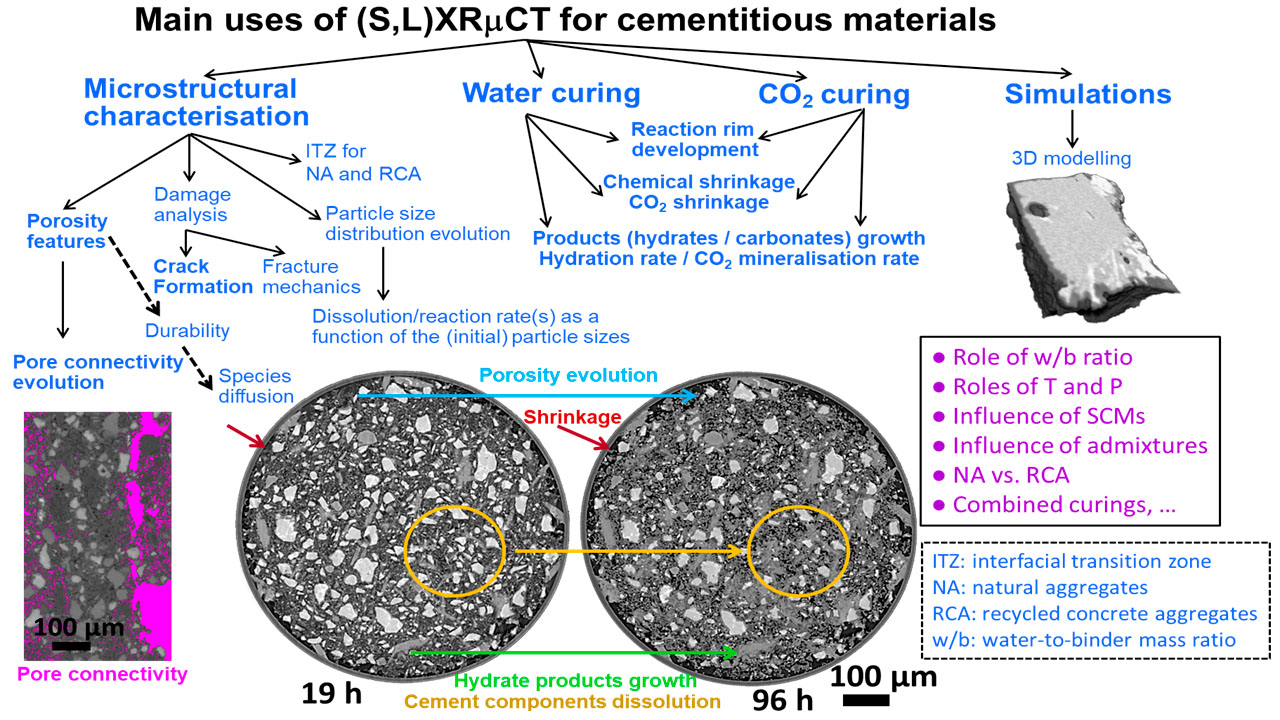
X-Ray Micro-Computed Tomography (XRµCT) Visualises the 3D microstructure of cementitious materials — including pore networks and connectivity — in real time and without damaging the sample.Together, these methods allow 4D (3D + time) insight into how cements evolve, harden, and interact with CO₂ at the microscopic level.
Novelty and Added Value
The X-SeeO₂ project builds on rapidly growing global research into CO₂ mineralisation and cement decarbonisation, areas currently gaining major attention from both academia and industry. While many emerging technologies focus on CO₂ curing, carbonated products, aggregates, clinker substitutes, or even biotechnological routes, optimisation remains limited by the complexity of cement systems and the empirical nature of most studies.
X-SeeO₂ introduces a unique, data-driven approach to overcome these challenges by integrating advanced X-ray diffraction and imaging techniques with world-leading cement science expertise. Through unprecedented access to large-scale research facilities, robust analytical workflows, and in-depth materials knowledge, the consortium will:
•Reveal how microstructures evolve over time and under different environmental conditions;
•Enable the design of novel, low-carbon cementitious materials with optimised performance;
•Support the development of predictive models for material behaviour; and
•Provide open, high-quality 4D datasets and quantification tools for the wider research community.
By combining access to cutting-edge experimental infrastructure with targeted expertise, X-SeeO₂ will push the boundaries of CO₂ mineralisation research and accelerate innovation in sustainable cement and concrete technologies.
Technological Breakthroughs
The X-SeeO₂ project introduces a series of first-of-its-kind advances that will redefine how CO₂ mineralisation and cement decarbonisation are studied. These breakthroughs combine high-throughput X-ray techniques, in-situ experimentation, and data-driven analysis to accelerate innovation in sustainable cement materials.
Together, these innovations position X-SeeO₂ at the forefront of cement decarbonisation research, enabling new materials, methods, and open data resources that will benefit the entire scientific and industrial community.
1
High-Throughput Synchrotron X-Ray Diffraction (SXRPD)
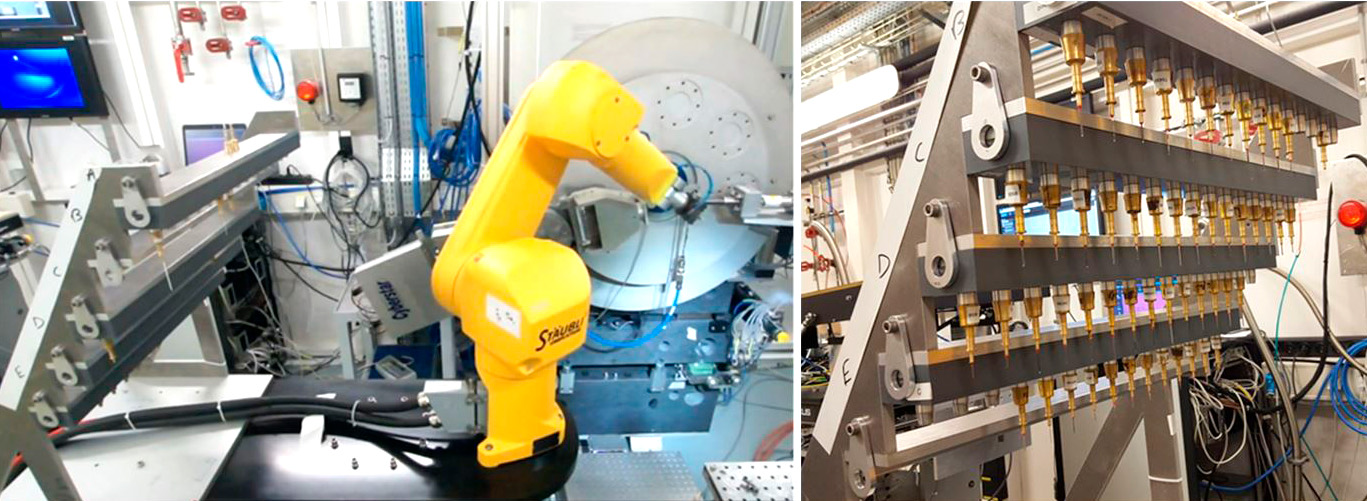
For the first time, high-throughput SXRPD will be applied systematically to cementitious materials, allowing rapid and precise analysis of large sample sets.
Unlike conventional methods limited to paste specimens, X-SeeO₂ will extend the technique to mortars, overcoming long-standing challenges related to sample dilution and complexity.
2
Real-Time SXRPD of Accelerated CO₂ Curing
Real-time SXRPD under controlled CO₂ pressures (up to 5 bar) and temperatures (up to 60 °C) has never been achieved before.
The project will adapt existing synchrotron gas-uptake cells to enable this, opening a new window into how carbonation reactions evolve in real time.
3
Multi-Scale X-Ray Tomography of Mortars and Pastes
Previous studies of CO₂-treated materials have focused mainly on pastes. X-SeeO₂ will expand the analysis to mortars, capturing microstructural changes such as cracking and carbonation shrinkage using advanced multimodal phase-contrast tomography at both laboratory and synchrotron scales.

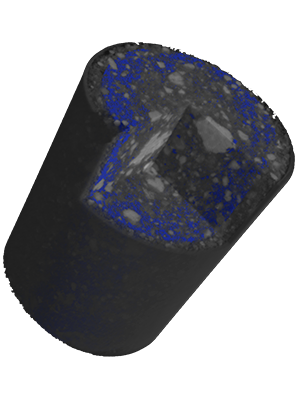
4
Real-Time Synchrotron Micro-Computed Tomography (SXRµCT)
A custom-built experimental cell will be designed for real-time 3D imaging of mortars during CO₂ uptake (up to 3 bar and 60 °C).
This will provide unprecedented insights into the microstructural evolution of cementitious materials during carbonation
5
Standardised Data Workflows and Open Access
To ensure comparability and transparency, X-SeeO₂ will develop robust, open-source data collection and analysis workflows for both X-ray diffraction and imaging.
These will establish community-wide standards, resolving inconsistencies between research groups and enabling reproducible science.

6
Mechanochemical Activation under CO₂
The project will pioneer the use of mechanochemical activation (MCA) under CO₂ to convert alkaline industrial wastes into highly reactive supplementary cementitious materials (SCMs).
This process could reduce global warming potential by up to 90% compared to conventional thermal treatments, supporting net-zero manufacturing

7
Accelerated Innovation via High-Throughput CO₂ Curing Studies
Combining high-throughput SXRPD with accelerated CO₂ curing, X-SeeO₂ will study blended systems containing both standard SCMs and CO₂-derived SCMs, dramatically speeding up the discovery of new sustainable cement formulations.

